The most popular types of Tampa breast implants type include saline, which are saltwater-filled, inserted empty and filled in place; Silicone (gummy bear), which are silicone gel-filled and pre-filled. Pros: Saline can be safer if ruptures (deflates visibly) and costs are often slightly lower. Pros: Silicone looks and feels more natural, lasts longer and are more durable. Cons: Saline feels and looks less natural; silicone rupture is possible and more difficult to detect.
Tampa Breast Implants Type – The Key Takeaways
When considering breast implants, the “best” option varies significantly depending on individual needs, body type, desired outcome, and health considerations. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, but understanding the different types of implants and their characteristics can help you make a more informed decision. Here’s a detailed look at the most common types of breast implants to help guide your choice:
- Silicone Gel Implants
- Saline Implants
- Structured Saline Implants
- Cohesive Gel “Gummy Bear” Implants
- Autologous Fat Transfer
Breast Implants Type – The Pros and Cons
1. Silicone Gel Breast Implants
Silicone gel implants are filled with silicone gel, which feels a bit more like natural breast tissue. Many women choose these implants because they tend to provide a smoother and more natural feel compared to other types. If the implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell or escape into the breast implant pocket, but it will not collapse.
Pros:
- Lower risk of rippling.
- Tend to feel more like natural breast tissue.
Cons:
- Requires a larger incision for placement.
- More difficult to detect leaks (requires regular monitoring with MRI or ultrasound).
2. Saline Breast Implants
Saline implants are filled with sterile salt water. They are inserted empty and then filled once they are in place, allowing for a smaller incision and easier size adjustments during surgery. If a saline implant leaks, the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
Pros:
- Smaller incision required.
- Adjustable size during surgery.
- Leakage leads to noticeable deflation, making it easier to detect issues.
Cons:
- Higher risk of rippling and folding.
- More likely to feel less natural compared to silicone.
- Lifespan is shorter (10-12 years average) compared to silicone
3. Structured Saline Breast Implants
A newer form of saline implants, structured saline implants, contains an inner structure that aims to make the implant feel more natural while maintaining the safety benefits of saline.
Pros:
- Designed to feel more natural than traditional saline.
- Still uses saline solution, which is safely absorbed by the body in case of leakage.
Cons:
- It can be more expensive than traditional saline implants.
- Relatively new on the market, so long-term results are less known.
4. Cohesive Gel “Gummy Bear” Breast Implants
These are form-stable implants that hold their shape even if the implant shell is broken. The silicone gel inside these implants is thicker than traditional silicone gel implants, which helps them maintain their shape but also makes them firmer.
Pros:
- Less likely to wrinkle or ripple.
- Maintains shape even if the shell breaks.
- Provides a very natural shape and slope.
Cons:
- Requires a longer incision for placement.
- Firmer feels may not appeal to everyone.
- If rotated, it may lead to an unusual appearance requiring surgical correction.
5. Autologous Fat Transfer
This technique involves liposuction to remove fat from parts of your body where there’s excess fat, such as your thighs or abdomen, and injecting that fat into your breasts. This is generally considered for moderate increases in breast size or to improve breast contour.
Pros:
- Uses your own body tissue.
- No risk of rejection or allergic reaction.
- The dual benefit of removing fat from unwanted areas.
Cons:
- Multiple procedures may be needed.
- Limited increase in size (usually one cup size).
- Potential for reabsorption of fat into the body over time.
Tampa Breast Implants Type – Choosing the Right Implants
1. Consult with a Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon
Their expertise will guide you through choosing an implant based on your body type, lifestyle, and aesthetic goals.
2. Consider Your Lifestyle
For example, athletes might prefer a more natural movement, which could influence implant choice.
3. Think About Future Maintenance
Consider how willing you are to monitor potential issues or undergo future surgeries if necessary.
4. Personal Preference
Ultimately, how you want your breasts to look and feel will significantly influence your decision.
Tampa Breast Implants Type – Popular FAQs
What’s the main distinction between silicone gel and saline breast implants?
Silicone gel implants use a cohesive silicone gel inside a silicone shell, while saline implants are filled with sterile saline after placement. Silicone often feels more like natural tissue; saline can be firmer and may show rippling.
Are silicone gel implants safer than saline?
Both are considered safe by major health authorities when implanted by a qualified surgeon. The choice depends on feel, risk tolerance for rupture, and patient goals. Rupture signs and monitoring differ by type.
How do structured saline implants differ from traditional saline implants?
Structured saline implants are filled with saline but include an internal structure to mimic the look and feel of silicone, aiming for a more natural feel and reduced ripple compared to traditional saline.
What are cohesive gel “gummy bear” implants?
They use highly cohesive silicone gel that sticks together (like a gummy bear). They tend to hold shape, resist leakage if ruptured, and can come in various shapes and sizes.
Do gummy bear implants feel more natural than silicone standard breast implants?
They often feel very natural and have a lower rate of visible rippling in many patients, but sensation and appearance vary by person and placement.
What is autologous fat transfer for breast augmentation?
It’s a procedure that uses a patient’s own fat from another part of the body, purified and injected into the breasts to add volume. No synthetic implant is used.
Who is a good candidate for autologous fat transfer?
Candidates with modest breast augmentation goals who have adequate donor fat and realistic expectations. It’s also popular for breast reconstruction and natural contouring.
How does recovery differ between implants (silicone, saline, structured) and fat transfer?
Implants require incision healing and may involve muscle or tissue stretching; fat transfer requires liposuction harvest and fat grafting with a healing period. Recovery times vary by technique and individual.
Which option gives the most natural look and feel?
Many patients report silicone gel implants feel most natural; cohesive gel can also feel natural, depending on placement. Fat transfer offers a natural look with your own tissue, but volume changes with weight.
How long do breast implants last, and when might they need replacement?
Implants aren’t lifetime devices. Most patients consider replacement or revision after 10–20 years, due to aging, shape change, or rupture (especially for saline if the shell leaks).
How is implant rupture detected for silicone vs. saline?
Saline ruptures are usually obvious (deflation). Silicone rupture can be silent or detected via imaging (MRI is often recommended for silicone implants at intervals). Structured saline and gummy bear implants have their own rupture considerations.
Are there differences in incision sites for these options?
Yes. Common incisions include inframammary (under the breast), periareolar (around the nipple), and transaxillary (armpit). The choice depends on implant type, anatomy, and the surgeon’s plan.
What are the main risks or side effects to consider?
Possible risks include infection, scarring, capsular contracture, changes in sensation, rippling, asymmetry, and need for revision. Fat transfer adds risks of irregular contour and fat absorption.
How much do these options typically cost?
Costs vary widely by region, surgeon, and technique. Silicone implants are typically more expensive than saline; structured saline can be similar to cohesive gel; fat transfer adds costs for liposuction and multiple sessions. Check for all-inclusive pricing and financing.
How should I start choosing the right breast implant option?
Start with a board-certified plastic surgeon consultation. Discuss goals (size, shape, feel), body type, skin quality, healing history, and budget. They can tailor a plan mixing implants or fat transfer to achieve your desired result.
What’s the difference between smooth and textured breast implants?
Smooth has a sleek surface; textured has a rougher surface. Pros: Textured may reduce implant movement in some placements; may lower rippling visibility in certain patients. Cons: Textured implants have a higher risk of rare complications and, in some rarer cases, lymphoma concerns (BIA-ALCL); not ideal for all patients.
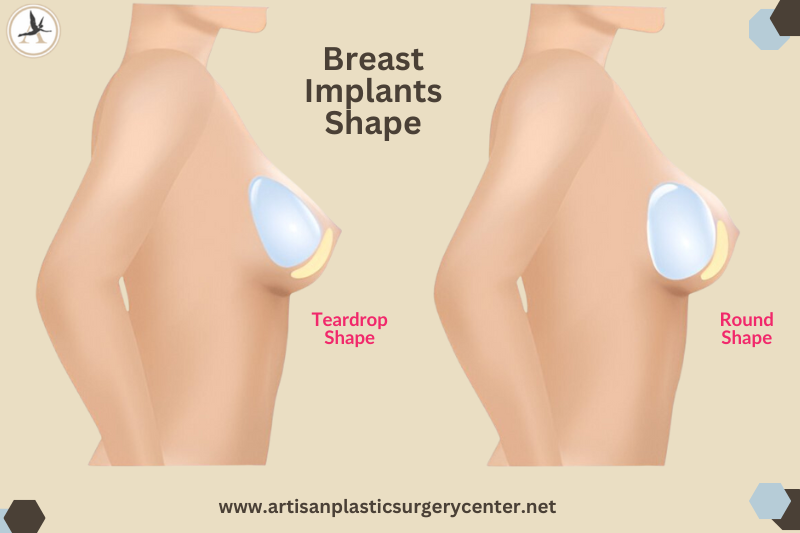
Round vs anatomical (teardrop) breast implants, which is better?
Round are symmetrical; anatomical mimic natural shape. Pros: Round can give more fullness from any angle; anatomical can look more natural when upright. Cons: Anatomical shapes can rotate (if textured, rotation risk exists) and may require precision sizing; round shapes are more forgiving.
What is a gummy bear (cohesive silicone) breast implant?
A cohesive silicone implant with a firmer gel. Pros: Very natural-looking shape, less likely to leak gel. Cons: More expensive; rupture signs may be less obvious; still requires monitoring.
Submuscular (behind chest muscle) vs subglandular (behind breast tissue) placement pros and cons?
Submuscular: Often better for coverage and lower capsular contracture risk; can reduce rippling. Cons: longer recovery, potential animation distortion.
On the other hand, Subglandular has quicker recovery, more natural upper pole fullness in some cases. Cons include more visible rippling in thin patients; possibly higher capsular contracture risk in some scenarios.
How do incision site choices affect breast implant type outcomes?
Incisions are separate from implant type, but influence feel and scarring. Common sites: inframammary, periareolar, transaxillary. Each has pros/cons for scar visibility and infection risk; choose based on anatomy and surgeon recommendation.
Do saline and silicone breast implants differ in rupture detection?
Yes. Saline: rupture is obvious as deflation. Silicone: rupture can be silent (no obvious change in shape/feel) and may require an MRI to detect.
Are textured breast implants more risky than smooth?
Historically textured implants carried a higher risk of BIA-ALCL (a rare lymphoma). Moreover, many markets have restricted or banned some textured options. Always check current safety data and surgeon guidance.
How long do implanted breasts typically last?
Implants aren’t lifetime devices. Most need replacement or revision after 10–20 years due to wear, rupture, or changing goals. Although. regular follow-up is important.
Are there differences in cost between breast implants type?
Yes. Silicone implants often cost more than saline; cohesive silicone and anatomically shaped implants can be pricier. Overall cost includes surgeon, placement, anesthesia, and follow-up.
Do implant types affect breast screening or MRI needs?
Implants may affect mammogram technique. Silicone implants generally require additional views; MRI is recommended periodically to check for silent ruptures (especially for silicone implants).
How do lifestyle and activity level influence breast implant choice?
Active individuals may prefer submuscular placement or certain shapes to minimize palpability and movement. Additionally, textured vs smooth, and surgeon recommendations may vary by activity.
Can implants change with pregnancy or weight changes?
The shape and fullness can be affected by weight fluctuations and hormonal changes. However, choosing placement, profile, and implant size with future goals in mind helps minimize shifts.
Are there non-surgical options?
Fat grafting (autologous fat transfer) is an option for volume and contour without implants, but it has its own limits (donor site, variable results). Not an implant type, but a consideration for a natural alternative.
How should I choose the right breast implant type for me?
It depends on anatomy, desired look, feel, budget, risk tolerance, and surgeon experience. In fact, a personalized consultation with imaging/sizing aids is essential to compare options and expectations.
Tampa Breast Implants Type – Complimentary Consultation in Florida, FL
Each type of breast implant procedure has its advantages and disadvantages. Contact us at (813) 971-2000 for a complimentary initial consultation to evaluate your case with Dr. Castor. Also, view our before-and-after breast augmentation gallery and our breast implant revision gallery.

